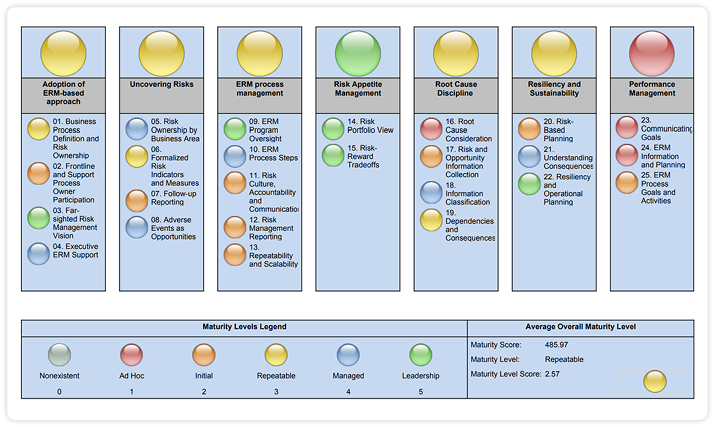
What is the Risk Maturity Model (RMM)?
The Risk Maturity Model for ERM serves as a free resource for risk and governance professionals to aid in planning, implementing and maturing enterprise risk management practices within their organizations. Those who utilize the RMM span across all industries and levels; from risk managers at financial institutions to C-level executives from energy or healthcare organizations and beyond.
The goal of the RMM is to serve as a benchmarking and educational tool for improving ERM practices and communication through an organization. Incorporating elements of existing best practice frameworks and ERM models, the RMM categorizes programs into one of five levels of maturity: (1) Ad-Hoc, (2) Initial, (3) Repeatable, (4) Managed and (5) Leadership. Achieving each level of added maturity indicates an organization’s success in achieving its business objectives and improving performance through the utilization of a risk-based mythology.
For details on the components of the Risk Maturity Model for enterprise risk management and how to leverage the results, please visit The RMM Explained and Results & Testimonials.
Understanding Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
At the core, enterprise risk management (ERM) is a method of systematically identifying, evaluating and prioritizing the activities and goals of an organization. Applying a common risk-based framework to the governance activities across departments, creates efficiency, drives better business decisions and strengthens strategic planning.
Whether analyzing risks, threats, opportunities or performance goals, a risk-based approach provides the framework needed to consistently connect and address overlapping concerns. Implementing a risk-based approach across departments and integrating it into the organization’s culture, is a fundamental component of a successful enterprise risk management program.
History of the RMM

The RMM authored by Steven Minsky, CEO of LogicManager is introduced in North America on November 27th, 2006. Its rapid adoption by organizations results in the incorporation of the RMM into programs from the IIA and AICPCU into their requirements and activities.
Risk Maturity Model Executive Summary (PDF)
Risk Maturity Model Full Edition (PDF)
LM authors its groundbreaking research on their data analysis of the organizations adopting the RMM and proving for the first time the direct evidence and correlation between a company’s credit rating and its ability to manage risk. The RMM is mapped to existing standards including ISO 310000, OCEG Red Book, BS31100, COSO, FERMA, and Solvency II to provide a roadmap for organizations to plan and achieve their risk management objectives.
The IIA’s International Professional Practices Framework (IPPF), effective Jan. 1, 2013, requires the role of internal audit to assess management’s ability to monitor and communicate risks in meeting the strategic objectives of the corporation. LogicManager publishes the Risk Maturity Audit Guide to help auditors review the effectiveness and sustainability of their organization’s risk management program. LogicManager research provides evidence that the Risk Maturity Model with LogicManager software eliminates legal liabilities and penalties due to risk negligence.
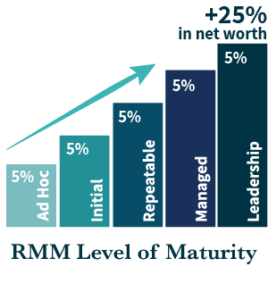
LogicManager's Risk Maturity Model makes history a second time, in a peer-reviewed independent study "The Valuation Implications of Enterprise Risk Management Maturity" which shows 25% market value premium for mature risk management practices. The Journal of Risk and Insurance publishes the findings that the AMBA-accredited MBA program at Queen's University Belfast research report recognized this important economic tool that is peer-reviewed for its validity. LogicManager's Risk Maturity Model goes global and becomes the largest database for benchmarking the effectiveness of Enterprise Risk Management programs.
The University of Pennsylvania's Wharton School ESG Analytics Lab selects LogicManager as research partner analyzing the relationship between Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) effectiveness and value investment outcomes.
In More Depth
LogicManager’s Risk Maturity Model (RMM) since 2006 has become the global standard for benchmarking the effectiveness of Enterprise Risk Management and is on the forefront of evidence-based research on corporate governance. In 2008, the RMM maturity index scores were the first to prove a direct correlation between the maturity of an ERM Program’s infrastructure and higher corporate credit ratings. In 2014, The Journal of Risk and Insurance (JRI) published the research findings of our partnership with Queens University that an organization’s index scores on the Risk Maturity Model are directly correlated to a 25% market value premium. In 2023, LogicManager has partnered with the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School to research the correlation between risk maturity and the success of ESG programs.
The Risk Maturity Model (RMM) assessment for enterprise risk management (ERM) helps risk management practitioners, senior leadership, auditors, and regulators evaluate the effectiveness and adequacy of an organization’s unique risk management program and determine where and how their program can improve. The Risk Maturity Model (RMM) is an umbrella ERM framework that covers ISO 31000, OCEG Red Book, BS 31100, COSO, FERMA and Solvency II standards. It allows organizations to use a single, effective risk management framework to manage their program while providing reports to meet any standard their internal or external stakeholders require.
ERM Program Audit Guide
The Audit guide is a valuable resource for your risk and audit teams to work together to make sure you are meeting the obligations of the board. Use the Audit Guide in conjunction with the RMM to confirm your organization’s ERM program is being measured effectively, accurately, and in alignment with the IIA’s standards.
Accreditation
Over 2,400 organizations have already baselined their risk maturity with the Risk Maturity Model.
 The Risk Maturity Model objectively measures the effectiveness of risk management program initiatives over time, provides a common language for risk management practitioners to share information internally, and enables an organization to benchmark their progress versus their peers in their industry and geography. The Risk Maturity Model is incorporated within the Associate in Risk Management-ERM (ARM-E) professional designation course material by The Institutes, the premier designation for all risk management professionals.
The Risk Maturity Model objectively measures the effectiveness of risk management program initiatives over time, provides a common language for risk management practitioners to share information internally, and enables an organization to benchmark their progress versus their peers in their industry and geography. The Risk Maturity Model is incorporated within the Associate in Risk Management-ERM (ARM-E) professional designation course material by The Institutes, the premier designation for all risk management professionals.
In 2014, the prestigious Journal of Risk and Insurance published the independent research study, “The Valuation Implications for Enterprise Risk Management Maturity.” This rigorous peer-reviewed academic study by Queens University AMBA accredited MBA program definitively quantifies a 25% market valuation premium for firms that have reached mature levels of enterprise risk management, as defined and measured by the Risk Maturity Model (RMM) for ERM.
In 2023 the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School selected LogicManager’s Risk Maturity Model (RMM) to investigate the relationship between Enterprise Risk Management and an organizations’ Environmental, Governance, and Social (ESG) initiatives.